All About Mining Difficulty: 2 Most Important Influencing Factors

Mining difficulty is a parameter that reflects the requirements for computing power to find a hash when creating a new block of transactions to the blockchain. With the growth of this parameter, equipment requirements also increase. Accordingly, miners spend more money on updating it, and the payback period grows. In this article, cloud mining provider, Hashmart.io, is going to talk about mining difficulty, how it is calculated, and what it affects.
What it is
In simple words, mining difficulty is a value that reflects the requirement for computing equipment to find a hash. The parameter is not fixed and is recalculated through a certain number of blocks.
With the introduction of new equipment with a high hash rate, the mining difficulty also increases. Consequently, the requirements for mining equipment increase. A kind of a technology race.
Difficulty analysis is an important part of work for a miner because the cost of purchasing equipment and the profitability of the process directly depend on this information.
Reason behind it
The difficulty is a necessary measure aimed at reducing the speed of emission against the background of an increase in powers in the cryptocurrency network. It is known that mining is the process of adding new blocks to the blockchain. To add each block, miners perform mathematical calculations using the equipment at hand. A reward is provided for each new block, the size of which periodically varies and depends on the cryptocurrency.
As with the printing of fiat money, cryptocurrency mining needs to be regulated. To avoid deflation and add more blocks than planned, the difficulty has been introduced. With its help, creators of digital coins solve two problems:
- They control the issue of coins and exclude exceeding the established limit (if any).
- Increase the value of cryptocurrency. The more difficult it is to mine coins, the higher the interest in them. This situation can be compared with “deficit” in ordinary practice. A product that is difficult to get is always more expensive.
The increasing difficulty stimulates manufacturers of computer technology to create powerful machines capable of more calculations per unit of time. For example, with the introduction of Bitcoin in 2009, there were no special requirements for CPU and GPU. With the increasing demand for mining, GPU manufacturers have begun some kind of competition for creating equipment with a higher hash rate. Miners became the main buyers of the GPU.
In 2014, ASIC miners with even more computing power appeared on the market. As a result, the mining difficulty jumped dramatically, and the old GPUs lost their previous efficiency. A new power race has begun, but already among ASIC developers.
What does it depend on?
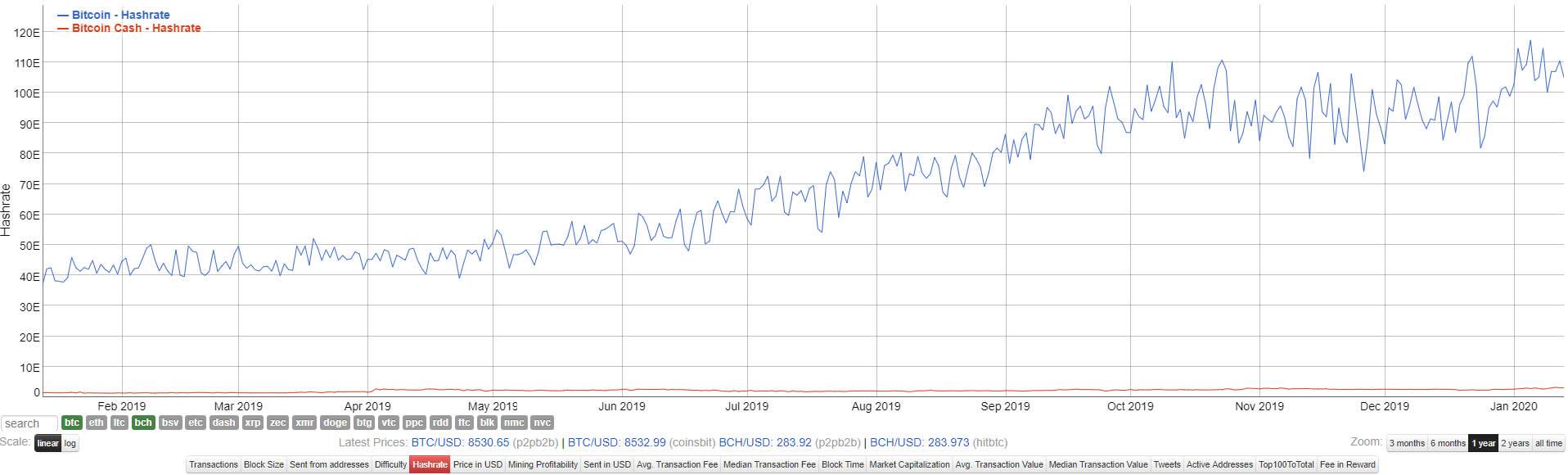
The mining difficulty is dynamic in nature due to the influence of two factors. The main one is the overall hash of the network, namely the total power of all equipment used for mining. The second factor is the time it takes to add a new block to the blockchain.
Both indicators are closely related. With the increasing demand for cryptocurrency, new participants are starting mining cryptocurrency. They use existing equipment, which leads to an increase in total power. Therefore, it takes less time to create a new block. As a result, the system adjusts the mining difficulty in order to keep the time indicator at approximately the same level.
The following patterns stand out here:
- If the hash rate is increasing due to an increase in the number of miners and the emergence of more powerful equipment, the time to create blocks is reduced, and the difficulty is increased.
- A decrease in the hash rate indicates a decline in interest in cryptocurrency and a decrease in the number of miners. It takes less time to create a block, and difficulty decreases.
Understanding such patterns is important for people planning to do cryptocurrency mining. The miner should see and analyze the situation several steps forward because the parameters of the cryptocurrency market are changing dynamically.
How to calculate mining difficulty
Mining difficulty is calculated using cumbersome mathematical formulas. However, for a general understanding of the process, it is enough to consider the situation with the example of one block. The essence of the calculation follows from the pattern discussed above.
The mining difficulty is equal to the product of two parameters — the time to create a block and the hash of the network. The first is measured in seconds, and the second in hashes. Therefore, the difficulty is measured by H/s. According to the formula, with an increase in the total power, the calculated parameter also increases.
In this way, the system equalizes the indicators and does not allow miners to mine coins in an accelerated mode. The balance of the system is maintained, and the risk of deflation and depreciation of the cryptocurrency is eliminated.
How mining difficulty changes
Recalculation does not occur instantly but after a certain number of blocks. For example, in the case of Bitcoin, this happens every 2016 new blocks. In the Bitcoin network, it takes about 10 minutes to create a new block. If the past 2016 blocks are created faster than the prescribed period, the mining difficulty increases to keep this parameter at a given level. In the event of a reduction in the total power of the equipment and an increase in the time to create a block, the difficulty will decrease. A similar principle applies to other cryptocurrencies, but the recalculation time may be different.

How mining difficulty affects profitability
As noted, mining is the process of creating new blocks by calculating the hash using special equipment (CPU, GPU, ASICs, etc.). As soon as a miner or a group of miners mine a new block, they are given a reward. The size of the reward is different for each cryptocurrency. For example, for Bitcoin, it is 12,5 coins. It takes 10 minutes to add a block, after which a new element of the chain is created, and miners receive a reward.
With an increase in hash rate, power also increases. You have to connect additional miners to add the block. As a result, the reward received is divided into a larger number of users. In addition, in mining pools, the proportional principle applies. The more power a participant gives, the larger the share of the reward he receives. Therefore, with increasing difficulty, miners are forced to buy new equipment, and this is an additional cost.
At the same time, the amount of reward is also decreasing. For example, for Bitcoin in 2019, the reward is 12.5 coins per block, but in 2020, it will be halved. This happens every four years. Consequently, the profit of miners is also reduced.
In other words, with the increasing mining difficulty, the following occurs:
- the size of the participant’s payments when working in the pool is reduced;
- there is a need to purchase equipment with a higher hash rate.
When calculating profitability, the difficulty is always taken into account. In addition, when buying equipment, it is important to take into account this parameter in the future and, accordingly, the increase in hash rate requirements. There are many cases when miners ordered expensive ASIC miners, which after some time lost their relevance.
Where to monitor mining difficulty
Many special resources are created to monitor the mining difficulty. The most convenient is bitinfocharts.com. The site provides detailed information on cryptocurrencies, block sizes, the speed of their creation, the size of the reward, etc. For example, to get data on Bitcoin mining difficulty, go to bitinfocharts.com/en/comparison/bitcoin-difficulty.html.
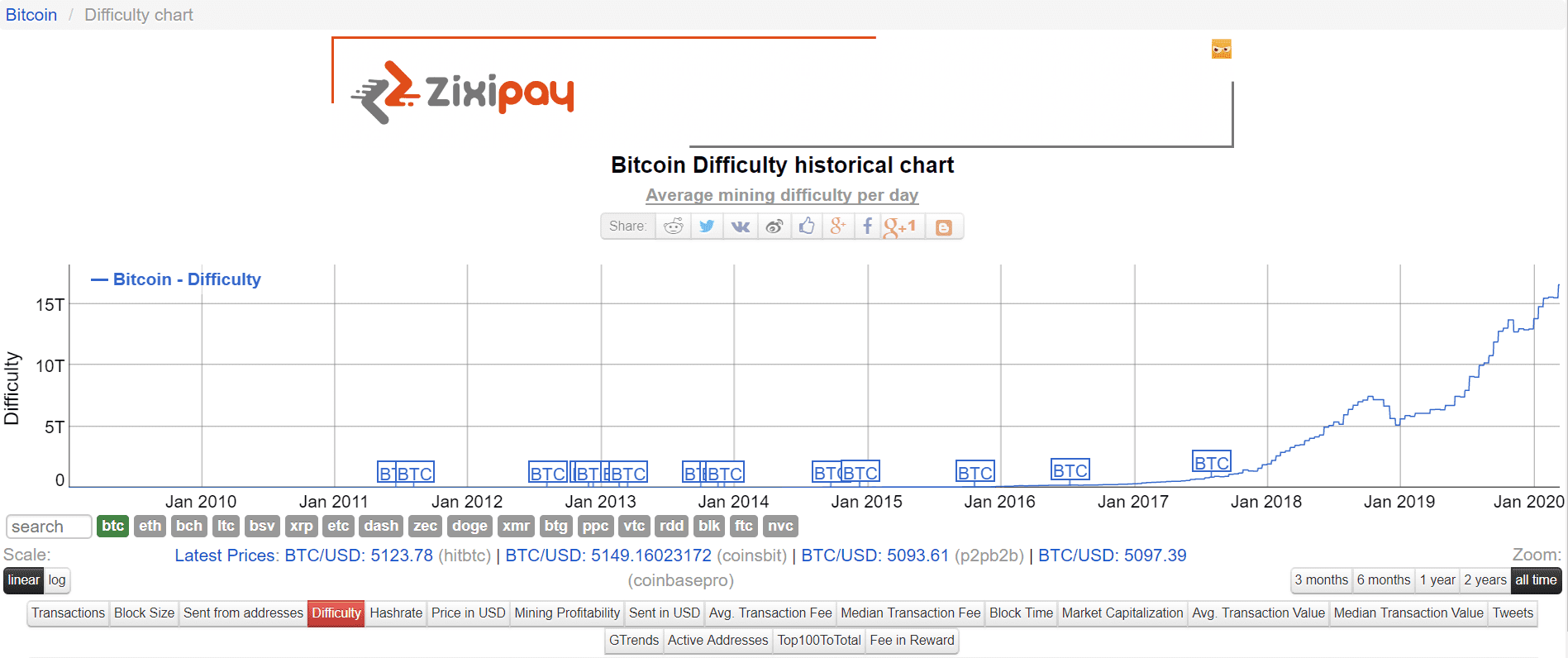
There will be a chart, where a dynamic change in mining difficulty is displayed. According to the information, you can draw conclusions about the jumps in the popularity of Bitcoin mining. The same information is easy to obtain on other digital coins.
Summary
Mining difficulty is an invariable element of mining that controls the value of cryptocurrency and protects it from deflation processes. The task of miners is to consider this parameter when calculating profitability. It is also important to remember the trend of this parameter to change with increasing demand and increasing power used for mining.